- Ctrl+C+Python
- Posts
- 🐍 Python Basics: Mastering Regex—Find, Match & Replace Like a Pro
🐍 Python Basics: Mastering Regex—Find, Match & Replace Like a Pro
Ever needed to search for patterns in text, validate emails, or extract specific information from a messy dataset? Regular expressions (regex) are the ultimate tool for handling text like a pro. Today, let’s break down Python’s re module and learn how to find, match, and manipulate text effortlessly. Let’s go! 🚀
Take your learning to the next level with quick, aesthetic coding tutorials on my YouTube channel! 🚀✨
🎥 Watch now: @CtrlCPython
Subscribe for bite-sized Python lessons with lofi vibes & clean code. ☕🎶
1. What is Regex?
Regular expressions (regex) are patterns used to search, match, and manipulate strings. Python provides regex support via the built-in *re** module.
To use regex, you need to import re first:

🔹 Searching with re.search()
re.search() scans a string for the first match of a pattern.

r"\$\d+"→ Matches a dollar sign ($) followed by one or more digits (\d+).
🔹 Finding All Matches with re.findall()
Use re.findall() to get all occurrences of a pattern.

🔹 Matching Patterns with re.match()
re.match() only checks if the start of a string matches the pattern.

If the string doesn’t start with "Hello", it won’t match.
🔹 Replacing Text with re.sub()
Use re.sub() to replace text that matches a pattern.

🔹 Using Regex with Groups
Use groups to extract specific parts of a match.
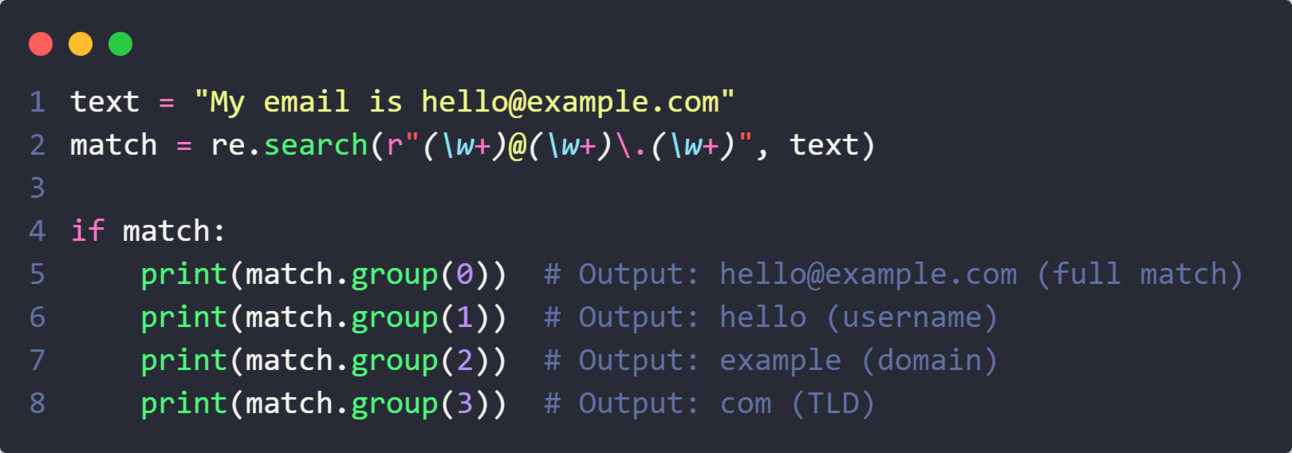
(\w+): group(1) → Matches the username(\w+): group(2) → Matches the domain(\w+): group(3) → Matches the TLD (like.com,.org)
2. Common Regex Patterns
Here are some powerful regex patterns to supercharge your skills:
Pattern | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Matches a digit (0-9) |
| Matches non-digit characters |
| Matches a word character (a-z, A-Z, 0-9, _) |
| Matches a non-word character |
| Matches whitespace (spaces, tabs, newlines) |
| Matches non-whitespace characters |
| Matches the start of a string |
| Matches the end of a string |
| Matches any character except newline |
| Matches 0 or more occurrences of the previous pattern |
| Matches 1 or more occurrences |
| Matches 0 or 1 occurrences (optional) |
| Matches n to m repetitions |
Example: Find all words that start with a capital letter:

3. Challenge: Regex Mastery!
Write a Python script that extracts all valid email addresses from a given text. Drop your solutions in the comments! 💡
🏆 Conclusion
That’s it for today! Regex is a powerful tool—once you master it, text processing becomes effortless.
What other Python basics do you want to learn about? Let me know in the comments! 🚀🐍
Happy coding! 🚀🐍
Digital Shade
Reply